PVD deposits allow a thermal functionalization of the surface on all kinds of substrate.
- Low emissivity coating (Au 99.99%, ε ≤0.1)
- High emissivity coating (black PVD or DLC, ε =0.8-1)
- Barrier layer
What is PVD coating?
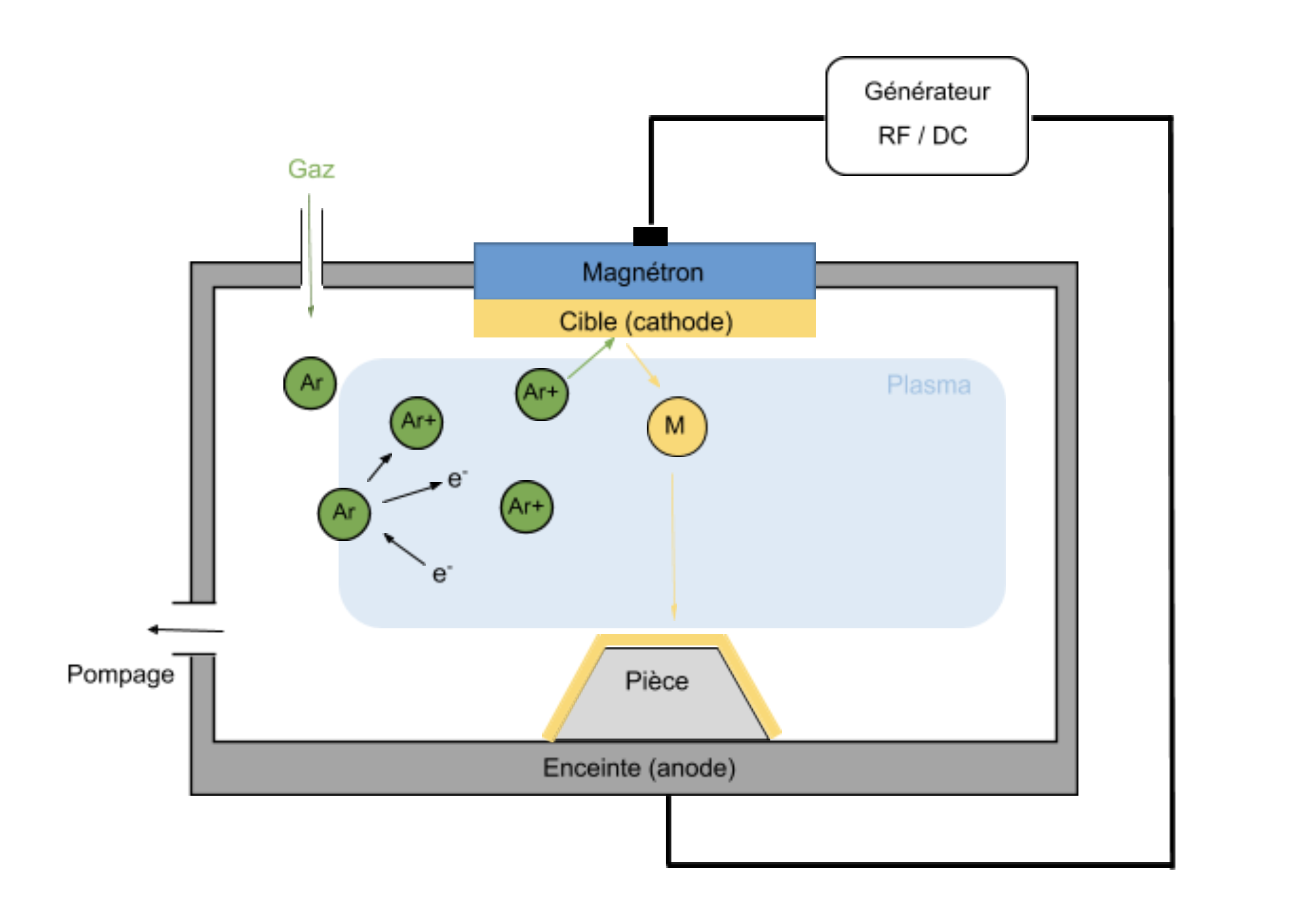
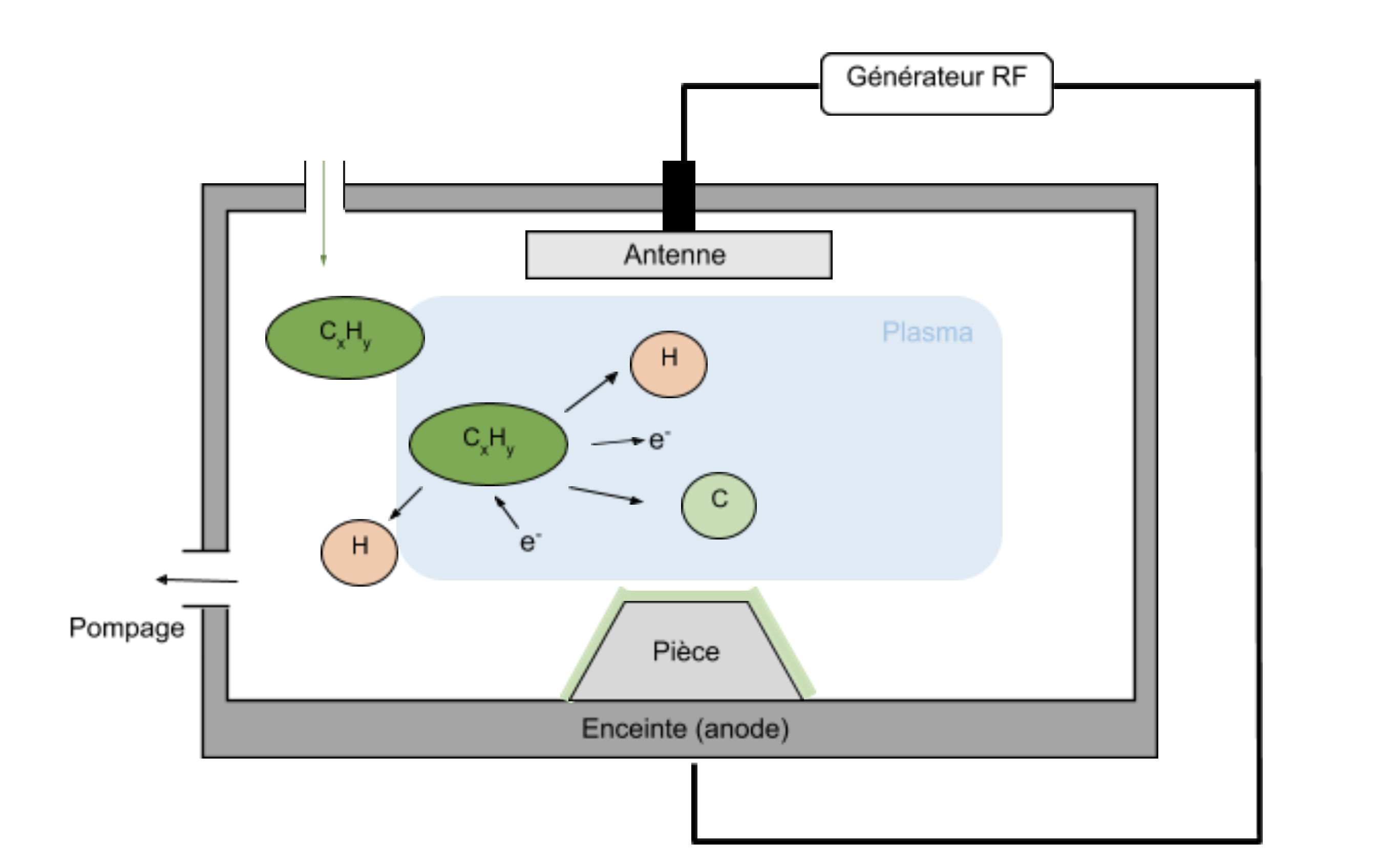
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a deposit coating process which allows to deposit under vacuum thin films of material using vapor.
The parts to be treated are placed in a vacuum machine.
After a gas is introduced, a plasma is created, and the positively charged ions are accelerated by an electric field onto the electrode, or ‘target’, which is negatively charged. The target is the material to be deposited.
The ions strike the target with sufficient a force so as to eject atoms. These atoms condense on the surfaces placed nearby and make up the coating.
To increase process speed, the targets are fixed on a magnetron which improves the efficiency of the process and renders it industrial.
This low temperature process allows the coating of all kind of materials on a wide range of substrates.
PVD metallization allows the deposition of a variety of materials such as layers of chromium, titanium, aluminum, copper, gold, silver or ITO.
Application examples
- Reflectivity
- Absorption/opacity
- Decorative/identification
- Galvanic substitute
- Conductivity
- Etc


